An ionizer in an air purifier releases charged particles, or ions, into the air. These ions attach to airborne particles, making them heavier and more likely to fall to the ground or stick to nearby surfaces. Whether do ionizers really work in air purifiers and how effectively they remove pollutants is a complex question we’ll explore in detail.
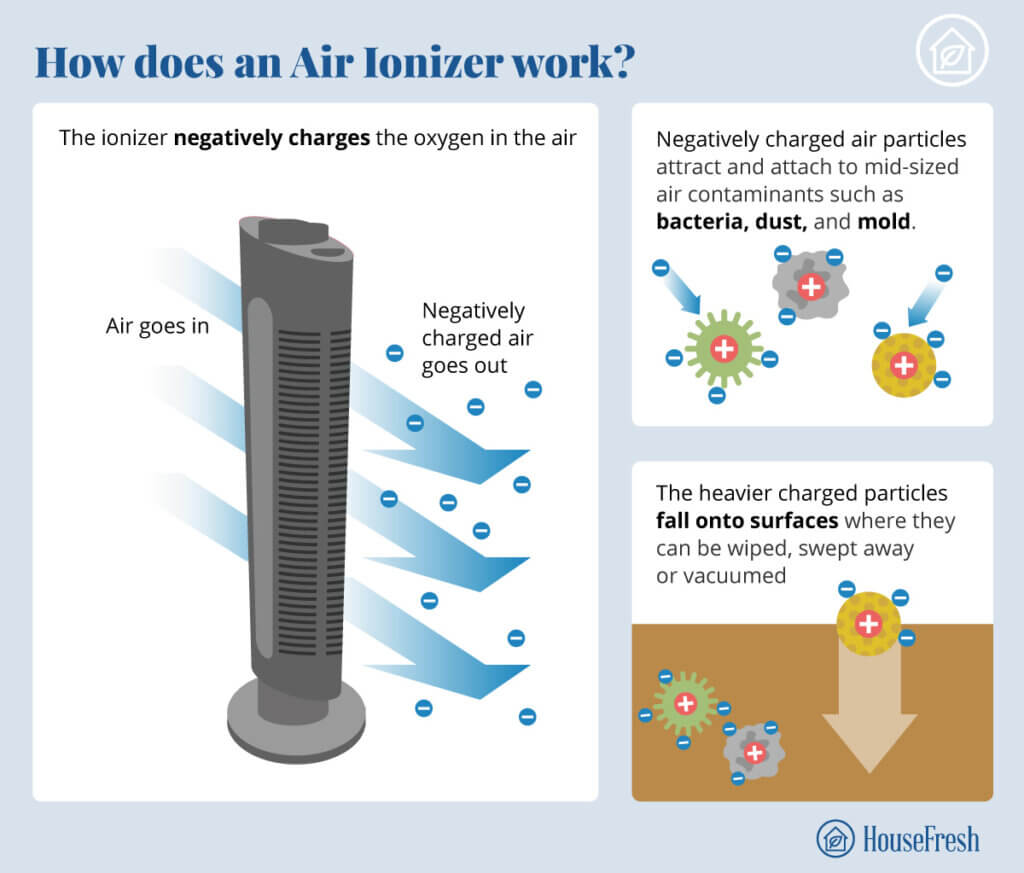
Image Source: housefresh.com
Fathoming Air Purifier Ionizers
Air purifiers are made to clean the air. Some use filters to trap bad stuff. Others use ionizer technology in air purifiers to change the particles in the air. These air purifiers are known as negative air ionizer pollutant removal systems.
How Air Purifier Ionizers Clean Air
How air purifier ionizers clean air? They work by releasing negative ions. These ions stick to things floating in the air, like dust, pollen, smoke, and germs. When the ions stick, the particles become heavier. Then, they fall to the ground or stick to walls and furniture.
The Science Behind Ionization
Ionization is the process of adding or removing electrons from an atom or molecule, giving it an electrical charge. In air purifiers, negative ions are typically produced. Let’s look closer at negative ion air purifier function.
Creating Negative Ions
Air purifier ionizers have a device that makes negative ions. This device uses electricity to split air molecules. When the air splits, it releases electrons that stick to other air molecules, making them negatively charged ions.
Attaching to Airborne Particles
These negative ions are released into the room. They quickly attach to particles floating in the air. This includes:
- Dust
- Pollen
- Smoke
- Pet dander
- Mold spores
- Viruses and bacteria
The Chain Reaction: Clumping and Settling
Once attached, the negative ions cause the particles to clump together. These larger clumps are heavier and less likely to stay in the air. They either:
- Fall to the floor.
- Stick to walls, furniture, or curtains.
- Get drawn back into the air purifier (if it also has a filter).
Are Ionizers Effective? Deciphering the Truth
The ionizer air purifier effectiveness question is complex. While ionizers can remove particles from the air, they don’t eliminate them completely.
Lab Tests vs. Real-World Use
Lab tests often show that ionizers can reduce particle counts in the air. However, real-world results can vary. The effectiveness depends on:
- The size of the room.
- How well the room is ventilated.
- The type and amount of pollutants.
The Issue of Surface Contamination
Ionizers don’t remove particles; they move them. This means that pollutants end up on surfaces in your home. You will still need to clean regularly to remove these settled particles.
The Role of Ozone
Some ionizers produce ozone as a byproduct. Ozone is a gas that can irritate your lungs and worsen respiratory conditions. The air purifier ionizer safety is a great concern.
Air Purifier Ionizer Benefits: Weighing the Advantages
Despite the drawbacks, air purifier ionizer benefits still exist.
- Particle Reduction: Ionizers can reduce the number of airborne particles, which may help people with allergies or asthma.
- Odor Control: Some users report that ionizers help reduce odors, although this effect may be temporary.
- Air Freshening: Negative ions may create a feeling of freshness in the air.
Air Purifier with Ionizer Pros and Cons: A Balanced Look
To make an informed decision, it’s important to weigh the air purifier with ionizer pros and cons.
| Feature | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Removal | Can reduce airborne particles. May help with allergies. | Doesn’t eliminate particles; they settle on surfaces. |
| Odor Control | May reduce some odors. | Effect may be temporary. |
| Air Quality | May create a feeling of freshness. | Can produce ozone, which is harmful. |
| Maintenance | Often requires less maintenance than filters alone. | Requires regular cleaning of surfaces to remove settled particles. |
| Cost | Can be less expensive than some high-end filter-based air purifiers. | Potential health risks from ozone production may outweigh the cost savings. |
Air Purifier Ionizer vs Filter: A Comparative Analysis
When choosing an air purifier, think about the air purifier ionizer vs filter options.
Filter-Based Air Purifiers
Filter-based air purifiers use filters to trap particles. HEPA filters are very common and effective at removing small particles.
- Pros:
- Effectively removes particles from the air.
- Doesn’t produce ozone.
- Cons:
- Filters need to be replaced regularly.
- Can be more expensive to maintain.
Ionizer Air Purifiers
Ionizer air purifiers use ions to change particles.
- Pros:
- Can reduce airborne particles.
- May help with odors.
- Cons:
- Doesn’t remove particles; they settle on surfaces.
- Can produce ozone.
Hybrid Systems
Some air purifiers use both filters and ionizers. These hybrid systems can offer the benefits of both technologies while minimizing the drawbacks.
Safety Considerations: Ozone and Health
Air purifier ionizer safety is important. Some ionizers produce ozone, which can be harmful.
The Dangers of Ozone
Ozone can irritate your lungs and worsen respiratory conditions. High levels of ozone can be dangerous, especially for people with asthma or other breathing problems.
Regulations and Standards
Some organizations have set limits on the amount of ozone that air purifiers can produce. Look for air purifiers that meet these standards. The California Air Resources Board (CARB) certifies air cleaners that meet ozone emission limits.
Choosing a Safe Ionizer
If you choose an air purifier with an ionizer, look for one that produces very little or no ozone. Check the manufacturer’s specifications and look for certifications from reputable organizations.
Tips for Using Air Purifiers with Ionizers Safely
If you choose to use an air purifier with an ionizer, follow these tips to minimize the risks:
- Choose a low-ozone model: Look for models certified by CARB or other reputable organizations.
- Ventilate the room: Open windows regularly to allow fresh air to circulate.
- Don’t use in small, enclosed spaces: Avoid using ionizers in small rooms with poor ventilation.
- Monitor for ozone: If you smell a strong chlorine-like odor, turn off the ionizer.
- Clean regularly: Wipe down surfaces to remove settled particles.
Do Ionizers Really Work in Air Purifiers? Summarizing the Evidence

The question of do ionizers really work in air purifiers is complicated. They can reduce airborne particles, but they don’t eliminate them. They can also produce ozone, which is harmful.
Making an Informed Choice
Before buying an air purifier with an ionizer, think about:
- Your specific needs and concerns.
- The size of the room.
- Your sensitivity to ozone.
- The availability of alternative air purification methods.
Air Ionizer Pollutant Removal: What They Can and Cannot Do
Air ionizers can help with certain pollutants but are not a solution for everything. Here’s a more detailed look at air ionizer pollutant removal:
Effective Against:
- Particulate Matter: Dust, pollen, pet dander, smoke particles are effectively charged and weighed down.
- Some Odors: Ionizers might neutralize some odor molecules, but this is often temporary.
Less Effective Against:
- Gases: Ionizers are generally not effective at removing gases like volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or carbon monoxide.
- Mold: While they can help settle mold spores, they don’t kill the mold source.
- Viruses and Bacteria: Effectiveness varies greatly, and they don’t sterilize the air. They merely cause these pathogens to settle.
Alternative Methods
For comprehensive air purification, consider these alternatives or complementary methods:
- HEPA Filters: Excellent for capturing particulate matter.
- Activated Carbon Filters: Effective for removing gases and odors.
- UV-C Light: Can kill bacteria, viruses, and mold spores.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is an air purifier ionizer?
A: An air purifier ionizer is a device that releases charged particles (ions) into the air to attach to pollutants, making them heavier and causing them to settle out of the air.
Q: Can I use an air purifier ionizer if I have asthma?
A: Use caution. Some ionizers produce ozone, which can worsen asthma symptoms. Choose a low-ozone model and monitor your symptoms closely.
Q: Who is most at risk from ozone produced by ionizers?
A: People with asthma, children, and the elderly are most at risk from ozone exposure.
Q: How often do I need to clean surfaces if I use an air purifier with an ionizer?
A: Clean surfaces regularly, at least once a week, to remove settled particles.
Q: What is the difference between an ionizer and an ozone generator?
A: An ionizer releases ions to charge particles, while an ozone generator intentionally produces ozone gas. Ozone generators are used for strong odor control but can be harmful if not used properly. Avoid using ozone generators in occupied spaces.
Q: Are there any air purifiers with ionizers that are safe for pets?
A: Look for low-ozone models and ensure adequate ventilation. Pets can also be sensitive to ozone.
Q: Is an air purifier with an ionizer better than one without?
A: Not necessarily. It depends on your needs. Filter-based air purifiers are generally safer and more effective for removing particles. Ionizers can be a helpful addition but should be used with caution.
Q: How do I know if my ionizer is producing too much ozone?
A: You may smell a strong, chlorine-like odor. You can also use an ozone meter to measure the ozone level in the air.
Q: Can I use an air purifier ionizer in my car?
A: Yes, some car air purifiers have ionizers. However, be mindful of ozone production, especially in the confined space of a car.
Q: What are some reputable brands of air purifiers with low-ozone ionizers?
A: Look for brands that are certified by CARB or other reputable organizations. Research user reviews and check the manufacturer’s specifications to ensure low ozone emissions.
My name is Carlos Gadd, and I am the creator of AirPurityGuide.com.. With a passion for footwear, I share my experiences, insights, and expertise about shoes. Through my blog, I aim to guide readers in making informed decisions, finding the perfect pair, and enhancing their footwear knowledge. Join me on this journey to explore everything about shoes!