Do you wonder what an air purifier does? An air purifier cleans the air in your home or office. It removes bad things like dust, pollen, and smells. How do air purifiers clean air? They pull air in and use special filters or other methods to catch tiny particles and gases. Yes, air purifiers can remove odors by trapping smell-causing particles. Are air purifiers safe? Most are very safe when used as directed. They help you breathe cleaner air. This guide will show you exactly how these machines make your air fresh and clean, step by step.
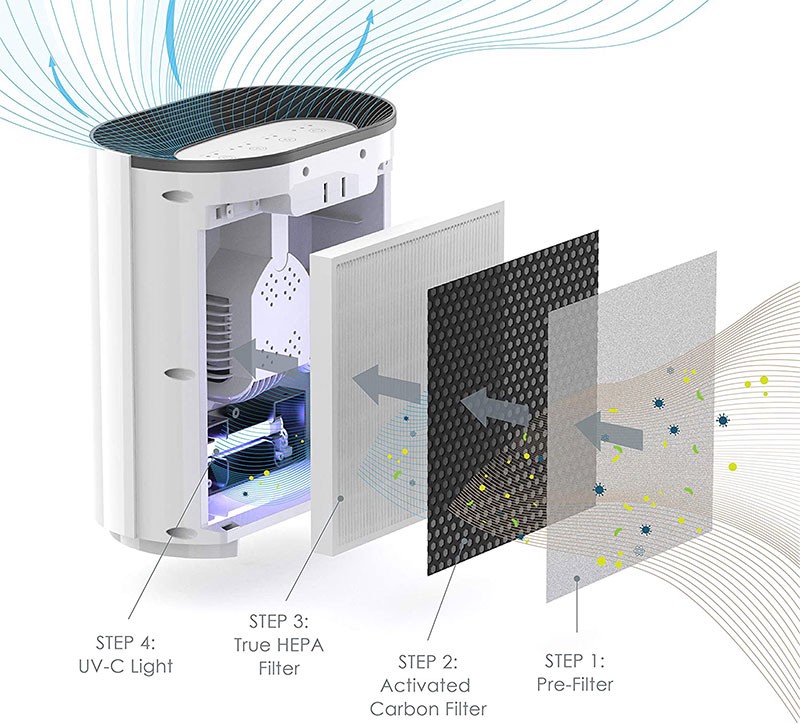
Image Source: aeno.com
Grasping the Need for Clean Air
Our homes often have more air pollution than we think. We bring in dust, dirt, and pollen. Pets add dander. Cooking creates fumes. Cleaning products release chemicals. All these things float in the air. They can make us sneeze, cough, or feel unwell. Some air particles are so tiny you cannot see them. But they can still affect our health. Air purifiers help fix this. They work hard to pull these bad things out of the air. This makes the air much safer to breathe for everyone. It is good for people with allergies or asthma. It also helps healthy people stay well.
The Basic Air Filtration Process: How Air Moves Through a Purifier
Air purifiers use a simple idea. They pull in dirty air. They push out clean air. Think of it like a big fan with a cleaning system inside.
Most air purifiers follow a clear path:
- Step 1: Air Entry: A fan pulls air from the room into the purifier.
- Step 2: Pre-filtering: The air first goes through a big filter. This filter catches large pieces.
- Step 3: Main Filtering: Next, the air moves to a finer filter. This filter catches very tiny things.
- Step 4: Other Cleaning: Some purifiers use more steps. They might use light or special charges.
- Step 5: Air Exit: The clean air then blows back out into the room.
This cycle happens again and again. It cleans all the air in the room over time. The air filtration process is central to how these machines work.
The Pre-Filter Function: First Line of Defense
Every good air purifier starts with a pre-filter. This is the first filter the air meets. Its job is simple but very important. The pre-filter catches large bits from the air.
What does a pre-filter stop?
- Big dust clumps
- Pet hair
- Lint from clothes
- Large bits of dirt
Think of it as a rough net. It stops the big stuff before it can get to the more delicate filters. Why is this so important? It protects the other filters. If large things get stuck in the main filters, they can get clogged quickly. This makes the purifier work less well. It also means you would have to change the expensive main filters more often. The pre-filter function helps your air purifier last longer. It also keeps it working at its best. Most pre-filters are washable. You can clean them yourself. This saves you money and effort. It is a key part of particulate matter removal.
HEPA Filter Technology: The Core of Particle Trapping
When people talk about air purifiers, they often talk about HEPA filters. HEPA stands for High-Efficiency Particulate Air. It is a very special type of filter. HEPA filter technology is seen as the gold standard for trapping tiny particles.
What is a True HEPA Filter?
A “True HEPA” filter is not just any filter. It must meet a strict rule. It must catch 99.97% of particles that are 0.3 microns in size. To give you an idea, a human hair is about 50 to 100 microns thick. So, 0.3 microns is super tiny! These particles include many common air pollutants.
How HEPA Filters Work: Not Just a Sieve
You might think a HEPA filter is like a screen. You might think it just has tiny holes. But it works in a more clever way. HEPA filters are made of a dense mat of fibers. These fibers are often glass or plastic. They are tangled together to form a thick, paper-like material. When air flows through this mat, particles get caught in a few ways:
- Direct Impaction: Larger particles hit the fibers directly and stick.
- Interception: Mid-sized particles follow the airflow. But their edges still touch the fibers and they get stuck.
- Diffusion: The smallest, lightest particles move in a wiggly way. They bump into the fibers and get trapped. This is often how particles smaller than 0.3 microns are caught.
What HEPA Filters Trap: Airborne Allergen Trapping
HEPA filters are excellent for airborne allergen trapping. They are highly effective at removing a wide range of airborne nuisances.
Common things HEPA filters catch:
- Pollen (from trees, grass, weeds)
- Dust mites and their waste
- Pet dander (tiny skin flakes from animals)
- Mold spores
- Smoke particles
- Some bacteria and viruses
Because of their ability to trap such small particles, HEPA filters are crucial for particulate matter removal. They make a big difference in air quality, especially for people with allergies or asthma. It is important to change HEPA filters regularly. They get full over time. When they are full, they cannot clean the air as well. The air filtration process relies heavily on a clean HEPA filter.
Activated Carbon Filtration: Tackling Smells and Gases
While HEPA filters are kings of particles, they cannot catch everything. They are not good at trapping gases or odors. That is where activated carbon filtration comes in. This type of filter uses a special material to trap molecules that cause smells.
How Activated Carbon Works: A Sponge for Gases
Activated carbon is a form of carbon that has been treated. This treatment makes it very porous. Think of it like a sponge with millions of tiny holes and tunnels. These tiny spaces give the carbon a huge surface area. One pound of activated carbon can have a surface area equal to many football fields!
When air passes through activated carbon, gas molecules are attracted to these tiny holes. They stick to the surface of the carbon. This process is called “adsorption.” It is like molecules getting glued onto the carbon. This is different from “absorption,” where something soaks into another.
What Activated Carbon Traps: VOC Capture Methods and Odor Elimination Principles
Activated carbon is very effective at VOC capture methods. VOCs are Volatile Organic Compounds. These are gases released from many common household items. They can cause odors and even health problems.
Things activated carbon filters excel at removing:
- Cooking smells: Like garlic, fish, or burnt food.
- Pet odors: From litter boxes, pet dander, or just the general smell of animals.
- Smoke smells: From cigarettes, cigars, or even wildfires.
- Chemical fumes: From cleaning products, paints, glues, and new furniture.
- VOCs: Like formaldehyde from building materials, or benzene from various sources.
Activated carbon filtration is key to odor elimination principles in air purifiers. Without it, your air might be free of particles but still smell bad. Like HEPA filters, activated carbon filters need to be changed. Once their tiny pores are full, they cannot adsorb more gases. They will stop working. Some purifiers combine HEPA and activated carbon in one filter unit. This makes the air filtration process very complete.
UV-C Light Sterilization: Zapping Germs
Some air purifiers add another layer of defense: UV-C light sterilization. This technology uses a special type of light to kill germs. UV-C light is part of the ultraviolet light spectrum. It is very strong. It can harm living things, even tiny ones.
How UV-C Light Works: Breaking Down DNA
The UV-C light inside an air purifier comes from a small lamp. When air flows past this lamp, the light shines on any airborne germs. This light attacks the DNA of these germs. DNA is like the instruction manual for a living cell. When its DNA is damaged, the germ cannot reproduce. It cannot make more copies of itself. This makes it harmless. It is effectively “killed.”
What UV-C Light Targets: Microbe Annihilation
UV-C light sterilization is mainly used to target microscopic living things.
It helps to destroy:
- Bacteria
- Viruses
- Mold spores
It is important to know that UV-C light does not trap particles or gases. It kills living things. So, it is often used with filters like HEPA and activated carbon. The filters catch the particles and gases. The UV-C light takes care of the germs that might pass through. This makes the air filtration process even more thorough. However, UV-C lights need to be handled with care. You should never look directly at a UV-C lamp. It can harm your eyes and skin. Also, some UV-C lamps can produce ozone, which is bad for lung health. Good air purifiers use “ozone-free” UV-C lamps. Always check for this feature.
Ionic Air Purification: Using Charged Particles
Another method some purifiers use is ionic air purification. This technology does not use filters in the same way. Instead, it uses electricity to clean the air.
How Ionic Purifiers Work: Giving Particles a Charge
Ionic purifiers have a special part called an ionizer. This part sends out tiny charged particles called ions. These ions are usually negatively charged. When these negative ions go into the air, they stick to airborne particles. Think of dust, pollen, smoke, or pet dander. When an ion sticks to a particle, that particle also becomes charged.
What happens next?
- Attraction: Once charged, these particles become attracted to grounded surfaces. This includes walls, floors, furniture, or a collection plate inside the purifier itself.
- Falling Out: The charged particles become heavier. They no longer float in the air. They fall out of the air onto surfaces.
- Collection: If the purifier has a collection plate, the charged particles are drawn to it like a magnet. They stick to the plate.
What Ionic Purifiers Target: Small Particles
Ionic air purification is good at removing very tiny particles. Things like:
- Fine dust
- Smoke particles
- Very small allergens
However, ionic purifiers have some drawbacks. They do not remove gases or odors. Also, if they do not have a collection plate, the particles just fall onto surfaces in your room. This means you will need to clean those surfaces more often. Some ionic purizers can also create ozone, a lung irritant. It is vital to choose an “ozone-free” ionizer if you opt for this technology. Many modern purifiers combine ionic technology with filters to make it more effective and safer. The air filtration process gets a boost when ions help clump particles together before they hit a HEPA filter.
Deciphering Combination Systems: The Power of Layers
Most top-performing air purifiers do not rely on just one cleaning method. They use a mix of technologies. This layering approach offers the best air purification. It combines the strengths of each method to tackle a wider range of pollutants.
Common Combinations in Air Purifiers
Here are some typical combinations you might find:
Pre-filter + HEPA + Activated Carbon: This is a very common and effective setup.
- Pre-filter handles large bits (pet hair, dust).
- HEPA filter removes tiny particles (pollen, dust mites, mold spores).
- Activated carbon handles gases and odors (smoke, VOCs, cooking smells).
- This combination is great for overall air quality. It covers particulate matter removal and VOC capture methods very well.
Pre-filter + HEPA + Activated Carbon + UV-C Light: Adding UV-C light zaps germs.
- It offers all the benefits of the above.
- Plus, it adds a layer of protection against bacteria, viruses, and mold.
- This is good for homes where sickness might be a concern. It also helps with airborne allergen trapping if mold is an issue.
Pre-filter + HEPA + Activated Carbon + Ionizer: The ionizer helps clump particles.
- The ionizer can make very fine particles stick together.
- This makes it easier for the HEPA filter to catch them.
- It can boost the efficiency of particulate matter removal. Always check for ozone-free ionizers.
Choosing a purifier with multiple stages ensures that many types of pollutants are removed. This provides the most complete air filtration process.
Particulate Matter Removal: A Deep Dive
Particulate matter refers to tiny solid or liquid pieces floating in the air. These particles are often invisible to the eye. They can be very harmful when breathed in. Air purifiers play a huge role in particulate matter removal.
Types of Particulate Matter
Particulate matter comes in many forms:
- PM10: Particles 10 micrometers or less in diameter. This includes dust, pollen, and mold spores.
- PM2.5: Particles 2.5 micrometers or less. These are much finer. They come from smoke, car exhaust, and industrial pollution. PM2.5 can get deep into your lungs.
- Ultrafine particles: Even smaller than PM2.5. They come from cooking, candles, and some industrial processes.
How Purifiers Remove Them
- Pre-filters: These catch the biggest particles (PM10 and larger). This is a vital pre-filter function.
- HEPA filters: These are the champions for PM2.5 and even smaller particles. As discussed, they trap 99.97% of particles 0.3 microns and larger. Their design ensures effective airborne allergen trapping and removal of many other fine particles.
- Ionic purifiers: These can help by charging very small particles. This makes them heavier, so they fall out of the air or stick to collection plates. This can aid in removing ultrafine particles that might otherwise escape filters.
The process of particulate matter removal is complex. It often needs a combination of filter types to be truly effective against all sizes of particles.
VOC Capture Methods: Clearing the Invisible Fumes
VOCs, or Volatile Organic Compounds, are gases that evaporate easily into the air. They are often odorless, but some have strong smells. They come from many sources in our homes.
Sources of VOCs
- Building materials: Paint, varnish, flooring, insulation.
- Furniture: New sofas, cabinets, carpets.
- Cleaning products: Sprays, disinfectants.
- Personal care products: Perfumes, hairsprays.
- Hobbies: Glues, craft supplies.
- Cooking: Certain food preparation.
- Burning things: Candles, fireplaces, smoking.
Many VOCs can cause health issues. These include headaches, nausea, or even more serious problems over time. This makes VOC capture methods very important.
How Purifiers Remove VOCs
- Activated Carbon Filtration: This is the primary method. The carbon acts like a sponge, adsorbing the gas molecules. The odor elimination principles come from the carbon trapping these smell-causing gases.
- Other Adsorbents: Some purifiers use other materials like zeolite or potassium permanganate. These also have properties that can trap or neutralize certain gases.
A good air purifier will have a thick layer of activated carbon. The more carbon, the better it can remove VOCs and odors. Replacing these filters on time is key for continued effectiveness.
Odor Elimination Principles: Making Your Home Smell Fresh
Bad smells can make your home feel dirty. Air purifiers can help a lot with odor elimination principles. Different technologies play different roles in this.
How Different Technologies Tackle Odors
- Activated Carbon Filtration: This is the superstar for smells. It directly adsorbs the gas molecules that cause odors. This is how it tackles cooking smells, pet odors, smoke, and chemical fumes.
- UV-C Light Sterilization: While not directly for odors, UV-C can kill bacteria and mold. These germs can produce bad smells. By killing them, UV-C indirectly helps with odor control.
- Ionic Air Purification: Some ionic purifiers can help by charging smell-causing particles. These particles then fall out of the air. This can help with some smoke or pet odors.
- HEPA Filters: HEPA filters do not remove gases or odors. They only remove particles. So, they won’t help with smells like stale air or chemical fumes. But they do remove things like pet dander, which contributes to a general “pet smell.” So, they play a supporting role in keeping the air truly clean.
For a complete odor elimination strategy, a purifier with a robust activated carbon filter is a must. The air filtration process must include a way to trap gas molecules, not just particles.
What to Look for When Buying an Air Purifier
Choosing the right air purifier can feel hard. Here are some key things to consider:
h4 Room Size
- CADR (Clean Air Delivery Rate): This number tells you how fast the purifier cleans air in a room. Look for a CADR that matches your room’s size. A higher CADR means it cleans faster.
h4 Filter Types
- True HEPA: Always look for “True HEPA” for excellent particulate matter removal, especially for airborne allergen trapping.
- Activated Carbon: Make sure it has a good amount of activated carbon for VOC capture methods and odor elimination principles.
- UV-C / Ionizer: If you want germ killing or extra particle removal, consider these. But always ensure they are ozone-free.
h4 Filter Replacement
- Cost and Frequency: Filters need changing. Find out how much new filters cost and how often you need to buy them. This is a running cost.
- Ease of Change: Can you change the filters easily yourself?
h4 Noise Level
- Quiet Operation: Air purifiers often run all the time. Look for models with low noise levels, especially for bedrooms.
h4 Energy Use
- Energy Star: Look for the Energy Star label. This means the purifier uses less electricity.
h4 Smart Features
- Auto Mode: Some purifiers have sensors. They can sense air quality and adjust fan speed on their own.
- Timers/Schedules: You can set them to run only at certain times.
A good air purifier is an investment in your health. Taking the time to pick the right one pays off with cleaner, fresher air.
Prolonging Your Purifier’s Life and Performance
To keep your air purifier working its best, you need to do some simple upkeep. Proper care ensures the air filtration process remains effective.
h4 Regular Pre-Filter Cleaning
- Wash or Vacuum: Many pre-filters are washable. Rinse them with water or vacuum them clean. Do this every 2-4 weeks, or more often if you have pets. This helps maintain the pre-filter function and protects the other filters.
h4 Timely Filter Replacement
- HEPA Filters: These usually last 6-12 months. The purifier might have an indicator light.
- Activated Carbon Filters: These also last 6-12 months, or less if you have many odors. They get full over time and stop working.
- UV-C Lamps: These need changing every 1-3 years.
Never wash HEPA or activated carbon filters unless the maker says you can. Washing them can ruin them. Not changing filters makes your purifier less effective. It also makes the fan work harder, which can use more energy or damage the motor.
h4 Keep the Airflow Clear
- No Obstructions: Do not block the air intake or outlet vents. Make sure there is space around the purifier. This lets air flow freely.
h4 Clean the Exterior
- Wipe Down: Dust builds up on the outside. Wipe it clean with a soft cloth now and then.
By following these simple steps, your air purifier will continue to provide clean air for a long time.
The Benefits of Clean Air
Having an air purifier in your home brings many great benefits. It is more than just removing dust. It truly improves your living space and well-being.
h4 Better Breathing and Health
- Fewer Allergies: By trapping pollen, dust mites, and pet dander, purifiers reduce allergy triggers. This means less sneezing, watery eyes, and stuffy noses. Excellent airborne allergen trapping is a big plus.
- Asthma Relief: People with asthma often react to tiny particles. Removing these can lead to fewer asthma attacks and easier breathing.
- Less Respiratory Irritation: Dust, smoke, and pollutants can irritate your lungs. Cleaner air means less irritation.
- Improved Sleep: If your breathing is better, you might sleep more soundly. Less congestion at night helps a lot.
h4 Fresher Smelling Home
- Odor Elimination: Activated carbon filtration attacks cooking smells, pet odors, and smoke. Your home will smell much fresher. This is a direct result of effective odor elimination principles.
h4 Reduced Dust and Cleaning
- Less Dusting: When the purifier catches dust from the air, less of it settles on your furniture. This means you have to dust less often! The efficient pre-filter function and HEPA filter technology directly lead to less visible dust.
h4 Protection from Germs
- Fewer Illnesses: UV-C light sterilization can kill airborne bacteria and viruses. This might help reduce the spread of colds and flu in your home.
h4 Peace of Mind
- Knowing Your Air is Clean: It is comforting to know you and your family are breathing clean air. This is especially true in areas with high outdoor pollution or if you have pets.
Investing in an air purifier is investing in a healthier, more comfortable home. The air filtration process works tirelessly to bring these benefits to you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
h5 Q1: How often should I run my air purifier?
A: It is best to run your air purifier almost all the time. Air quality changes throughout the day. Running it constantly ensures continuous cleaning. Most modern purifiers are energy-efficient and quiet enough for constant use.
h5 Q2: Can an air purifier remove all pollutants?
A: No air purifier can remove 100% of all pollutants. However, a good multi-stage air purifier, especially one with HEPA filter technology and activated carbon filtration, can remove a very high percentage of common particles, allergens, odors, and gases. It greatly improves indoor air quality.
h5 Q3: Do air purifiers help with pet odors?
A: Yes, absolutely! Air purifiers with robust activated carbon filtration are excellent for pet odors. They can trap the gas molecules that cause these smells. HEPA filters also help by removing pet dander, which contributes to the overall pet smell. This is a prime example of odor elimination principles at work.
h5 Q4: What is the difference between an air purifier and a humidifier?
A: An air purifier cleans the air by removing particles and gases. A humidifier adds moisture to the air. They do very different jobs. You can use both at the same time if needed.
h5 Q5: Do ionic air purifiers produce ozone?
A: Some older or cheaper ionic air purifiers can produce ozone, which is bad for health. Always choose an ionic purifier labeled “ozone-free” to ensure it is safe. Reputable brands ensure their products meet safety standards.
h5 Q6: How long do air purifier filters last?
A: Filter life depends on the type of filter, how often you use the purifier, and your air quality. Pre-filters can often be washed and reused. HEPA and activated carbon filters typically last 6-12 months. UV-C lamps last 1-3 years. Always check your specific model’s manual for exact replacement times.
h5 Q7: Where should I place my air purifier?
A: Place your air purifier in the room where you spend the most time, like a bedroom or living room. Put it on a flat, open surface, away from walls or furniture that might block airflow. Center placement is usually best for the air filtration process.
Concluding Thoughts: Breathing Easier
Air purifiers are much more than simple fans. They are clever machines that use advanced technologies to make the air we breathe safer and cleaner. From the basic pre-filter function to the powerful HEPA filter technology, the gas-grabbing activated carbon filtration, the germ-killing UV-C light sterilization, and the particle-clumping ionic air purification – each step plays a vital role.
The entire air filtration process is designed to remove a wide range of pollutants. This includes fine particulate matter removal, effective VOC capture methods, excellent airborne allergen trapping, and comprehensive odor elimination principles. By layering these systems, modern air purifiers offer a complete solution.
Investing in an air purifier means choosing better health for yourself and your family. It means cleaner lungs, fewer allergy symptoms, and a fresher-smelling home. Take the step to learn more, choose wisely, and breathe easier every day.
My name is Carlos Gadd, and I am the creator of AirPurityGuide.com.. With a passion for footwear, I share my experiences, insights, and expertise about shoes. Through my blog, I aim to guide readers in making informed decisions, finding the perfect pair, and enhancing their footwear knowledge. Join me on this journey to explore everything about shoes!